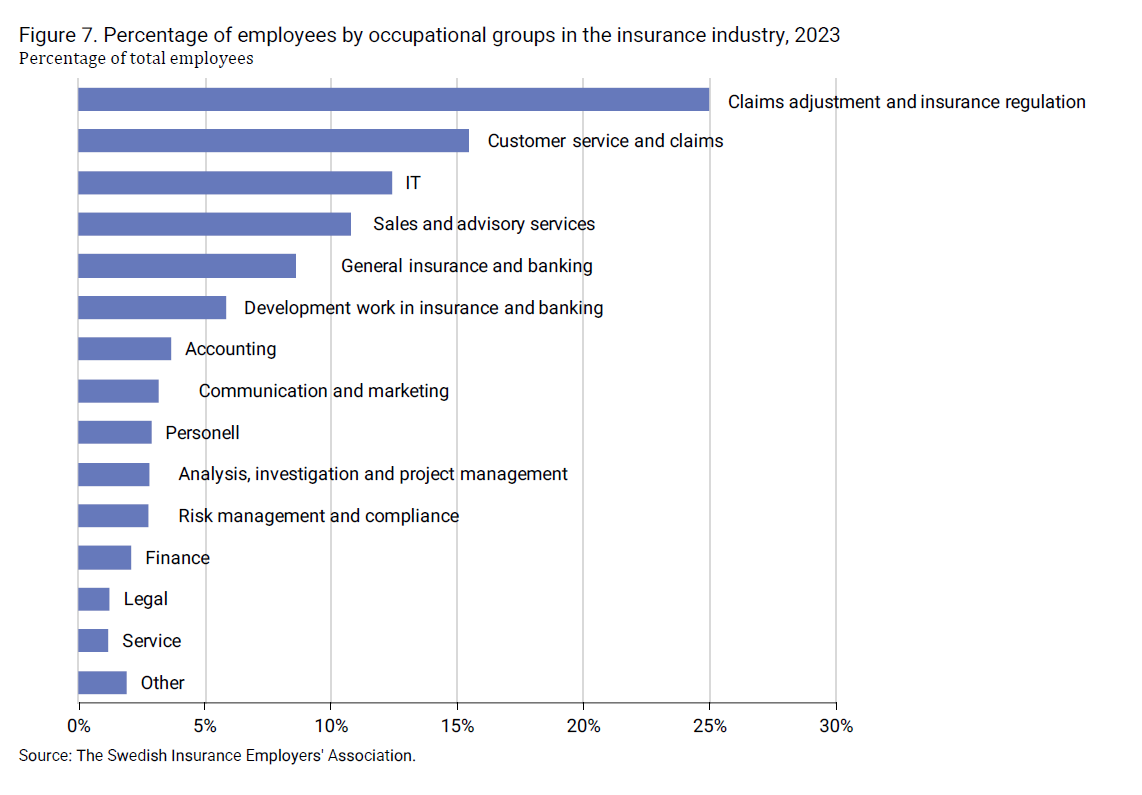
The Swedish insurance industry comprises 31 life insurance companies, 14 occupational pension companies, 202 non-life insurance companies, and 24 mutual benefit associations. Out of these 271 insurance and occupational pension companies, 34 are foreign-owned and represented in Sweden through branches or agencies. The number of foreign companies has re-mained largely unchanged over the years. Most companies are either larger nationwide or smaller local companies.
The number of companies has varied over the years, but compared to 2017, the number of companies has decreased by 22 per cent. It is primarily mu-tual benefit associations that have become fewer, and according to current legislation, mutual benefit associations are supposed to be phased out gradu-ally. Occupational pension companies have emerged since 2020. These are former insurance companies that have converted into occupational pension companies. The regulations differ between insurance companies and occupa-tional pension companies. Insurance companies are governed by the Insur-ance Business Act, while occupational pension companies are governed by the Occupational Pension Companies Act, which was introduced in late 2019.
The industry employs nearly 24,000 people, which corresponds to approxi-mately half a per cent of the total number of employees in the Swedish la-bour market. While the number of companies in the insurance industry has decreased by 22 per cent since 2017, the number of employees has increased by 22 per cent.
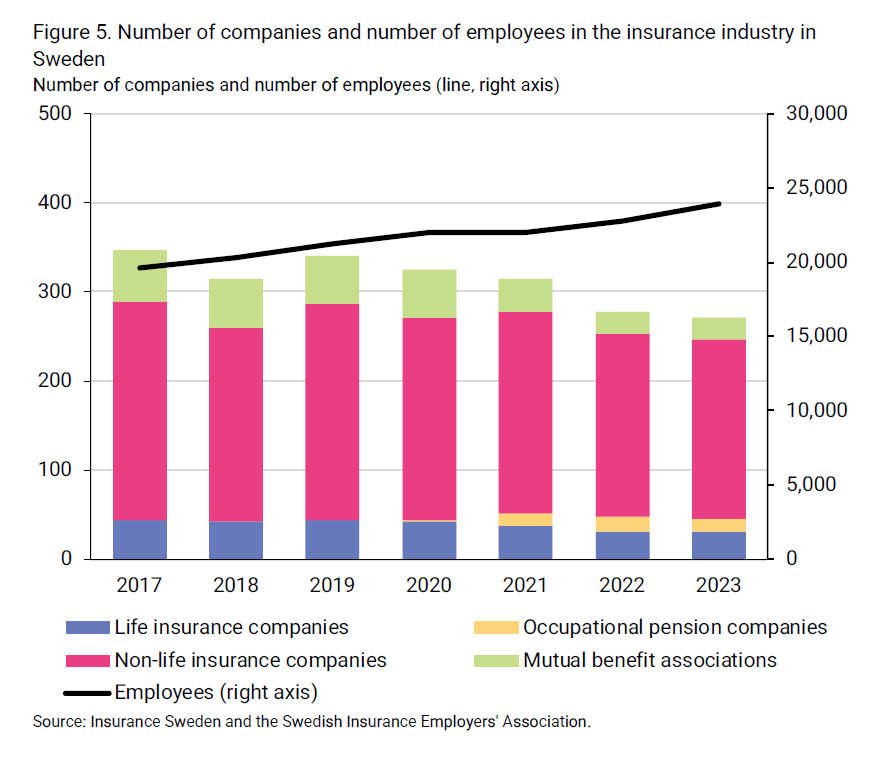
The Swedish insurance industry has a relatively even gender distribution. In 2023, over half, 54 per cent, of the employees in the industry were women. The proportion of women has consistently been slightly higher than the pro-portion of men since the early 2000s.
The proportion of female managers has been gradually increasing over time. In 2002, just over 36 per cent of managers were women. In 2023 the propor-tion was 47 per cent, which means close to half.
Both the proportion of women and the proportion of female managers are higher in the insurance industry than the average in the business sector, where 39 per cent of the employees are women and 37 per cent of the man-agers are women.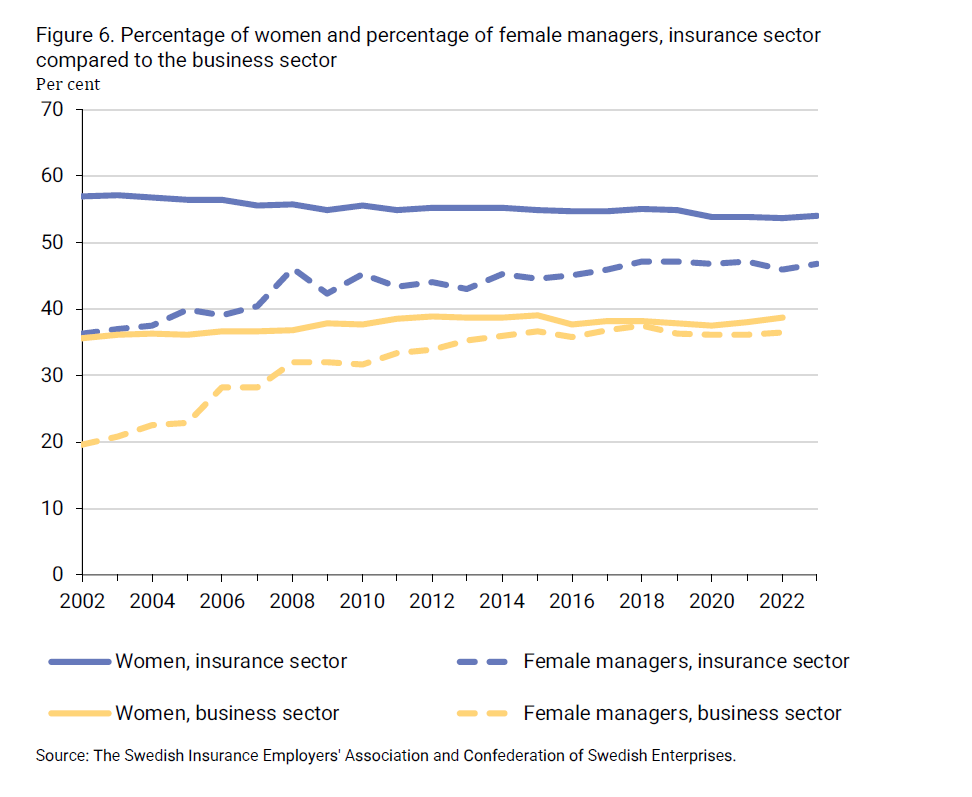
A quarter of the employees in the insurance industry are handling claims and working with insurance regulation. This occupational group includes investi-gations into the causes and liability of damages, as well as services involving risk assessments and analysis of reinsurance for other companies. Certain specialized professions, such as actuaries (insurance mathematicians), are also part of this occupational group. Other common occupations include cus-tomer service and sales, which are carried out by around 15 per cent of em-ployees, followed by IT work (12 per cent) and sales and advisory roles (11 per cent).