The vast majority of all employees in Sweden have an occupational pension insurance. Occupational pension is a supplement to the national public pension and has become increasingly important for the total pension of many individuals over time.
The Swedish pension system is summarized in the figure below where “the base” of the triangle (both yellow areas) illustrates the national public pen-sion consisting of income pension and premium pension. In addition, there are tax-financed benefits for pensioners and inheritors. The Swedish Pen-sions Agency manage both the income-based pension and the tax-financed benefits.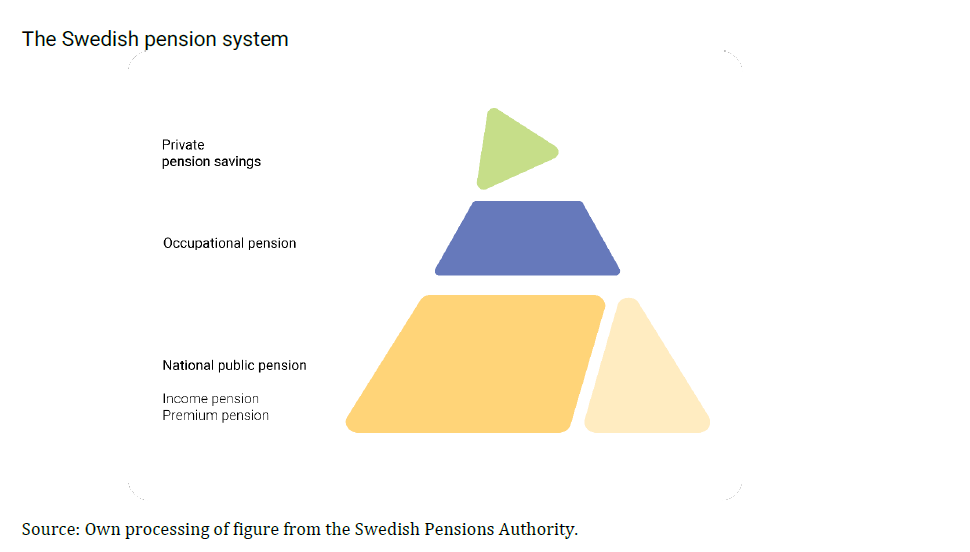
Occupational pension is a complement to the national pension and can be se-cured by employers in several ways. The most common way is for the em-ployer to pay premiums into a pension insurance offered by life insurance and occupational pension companies, with the employee as the beneficiary. Other methods include employers securing their occupational pension com-mitment internally by making a reservation of the pension obligations in the company's balance sheet or making contributions to a pension foundation. Until 2016, there were tax incentives for private pension savings through a tax deduction against income. Today, only self-employed and individuals lacking occupational pensions through their employments have the possibil-ity to make a tax deduction for private pension savings. Life insurance com-panies offer sole traders and individuals the opportunity to sign up for a pri-vate pension insurance.
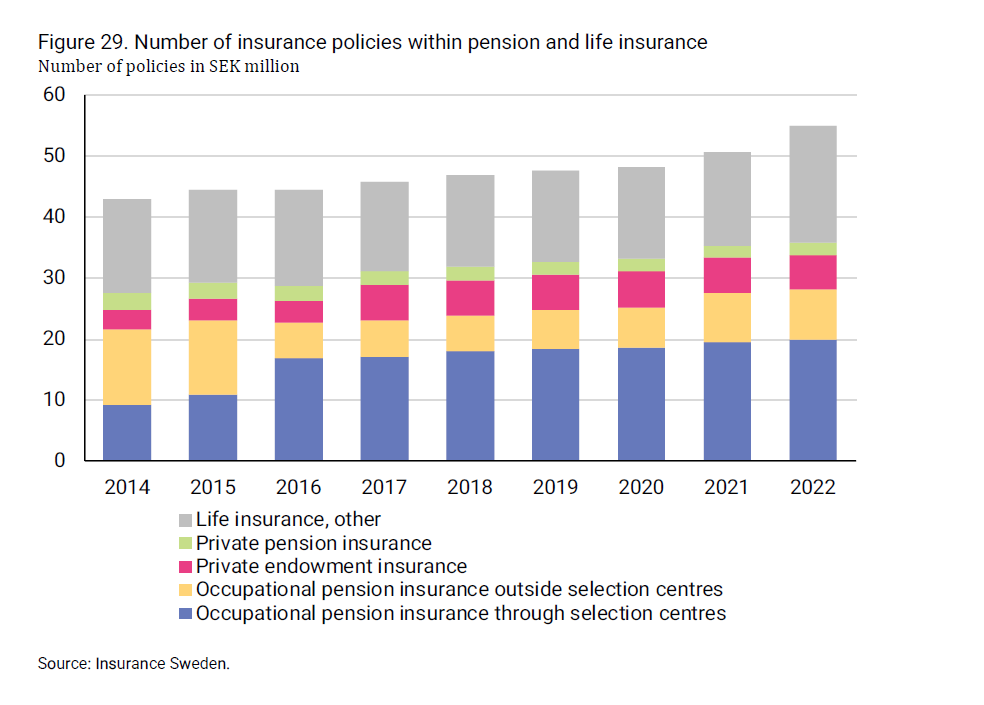
Within pension and life insurance, there are many various types of insurance policies that provide payments in connection with retirement, as well as var-ious forms of savings.
Occupational pension insurance is a pension insurance that is related to the employment where the insured person's employer has undertaken to pay all premiums for the insurance. The employee is the insured person and bene-ficiary of the insurance, while the employer is typically the policyholder of the insurance. If a person has had multiple employers throughout their life, there may be several different occupational pension agreements.
Insurance savings can be done in a private endowment insurance or a pri-vate pension insurance. An endowment insurance is a form of savings that can be bought by both individuals and companies. The savings are invested in equities, funds, and other securities. Private pension insurance is a private pension savings with a tax deduction where the savings are locked in the account until the policyholder reaches the age of 55. Today, only self-em-ployed and individuals lacking occupational pensions have the possibility to make a tax deduction for private pension savings.
At the end of 2022, there were a total of nearly 51 million insurance policies within pension and life insurance. More than half (55 per cent) of these poli-cies are occupational pension insurance. In addition, there were 5.7 million private endowment insurances and nearly 2 million private pension insur-ances.